Why is labeling medical devices important?
Medical devices is actually controlled communication tools that guarantee their safe, appropriate, and legal use.
conveys:
What the gadget is meant to do
Who should use it?
How to use it securely
Recognized risks, cautions, and warnings
Identity and accountability of the manufacturer
Mislead medical professionals and patients
cause serious health risks or harm
Restrict market access, recalls, and regulatory fines.
Before and after a product’s launch, regulators such as the FDA and EU officials closely examine it.
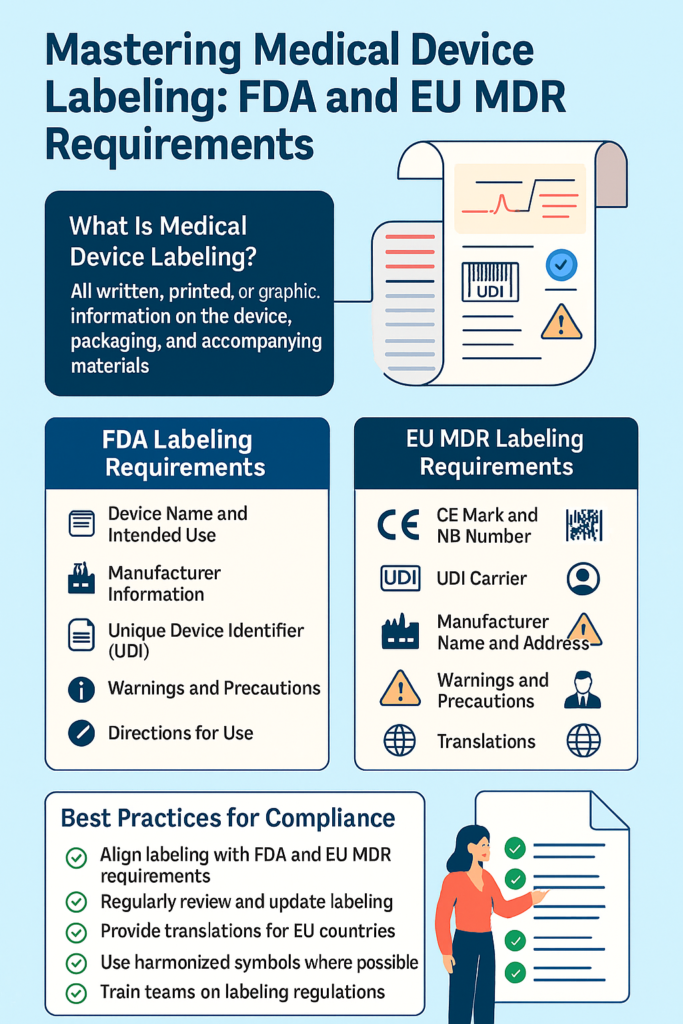
Labeling refers to any written, printed, or graphic content provided with the device—whether appearing on the device itself, its packaging, or accompanying accessories.
Labeling consists of:
The product’s
Packaging
User Guide or Instructions for Use (IFU)
Manuals for quick starts
brochures containing the device’s claims
Web data (if pertaining to the use of the device)
???? Key point: It includes any information that may affect how the device is used safely and effectively.
???????? FDA Guidelines for Medical Devices
Under 21 CFR Part 801, the FDA (U.S. Food and Drug Administration) controls the of medical devices.
✅ 1. The Definition
“Any written, printed, or graphic information on any label, container, wrapper, or item that comes with it.”
As a result, it comprises
The product’s
External packaging supplies
Useful Instructions (IFU)
Any advertising materials that contain details about the device
✅ 2. The Most Important FDA Requirements (Simplified)???? a) Device Name and Purpose
The device’s description and usage instructions must be made clear.
Avoid using terms that are unclear or deceptive.
For instance, “Single-use sterile dressing for the treatment of minor burns and abrasions.”
???? b) Details of the Maker
The manufacturer’s full legal name and address.
To distributors and packers as well.
If there is a problem, it traces it back.
?????? c) UDI, or Unique Device Identifier
Regulators and medical professionals can track the device using the UDI, a unique code.
Both machine-readable (barcode) and human-readable versions must be shown on the label.
Goal: Supports adverse event monitoring, recalls, and counterfeiting prevention.
???? Visit the FDA UDI System Guide to learn more.
???? d) Cautions and Advisements
must include a list of all known risks, hazards, or situations where the device shouldn’t be used.
prevents abuse or mishaps.
???? e) Usage Instructions
Easy-to-follow, detailed usage instructions.
It must be easy enough for the patient, nurse, or doctor who will be using it.
✅ 3. FDA Labeling Errors
❌ Exaggerating the benefits of devices without supporting clinical data Incorrect or absent UDI placement Not updating labeling when design or risk management changes
EU MDR Regulations for Medical Devices
It is strictly regulated in the EU by the EU MDR (Regulation 2017/745).
✅ 1. What Requirements Does EU MDR Have?
EU MDR Annex I, Chapter III must give users the details they require for:
Device identification
Use that is both safe and efficient
The ability to trace
✅ 2. Crucial EU MDR Labeling Requirements You Need to Add? a) CE Mark with Notified Body Number
Your device’s compliance with EU law is confirmed by the CE Mark.
The CE Mark must be displayed next to the notified body’s identification number if one is involved.
???? b) Manufacturer’s Name and Address
For accountability, much like the FDA.
The complete name and legal address of the manufacturer must be included.
???? c) The device, package, and IFU as necessary must have the UDI Carrier (Barcode and Human-Readable).
allows the device to be traced throughout Europe using the EUDAMED database.
???? d) Cautions, Advisements, and Restrictions
clear and concise description of the dangers and restrictions.
must be consistent with the goals you have outlined in your risk management file.
???? e) Authorized Representative Information (for Non-EU Manufacturers)
You must designate an authorized representative if your company is not in the EU.
The labeling must include their contact information.
???? f) Translations into Official Languages
IFUs and labeling must be available in the official languages of each EU member state where the device is sold.
???? g) Pictograms and Harmonized Symbols
To ensure clarity and minimize translation requirements, use EU-harmonized symbols (such as expiration date, single-use, and sterile).
must adhere to recognized guidelines such as ISO 15223-1.
✅ 3. EU MDR IFU Conditions
It must contain:
Description of the device
The intended use
Contraindications and indications
Information about risks
Comprehensive usage guidelines
Instructions for maintenance
???? The Connection Between Labeling and Post-Market Surveillance and Risk Management
Labeling is not a stand-alone activity. It is closely related to:
Risk management (ISO 14971): Safety information and known hazards must be listed on labels.
Post-Market Surveillance (PMS): If new risks emerge after launch, your labeling needs to be updated.
Correcting labels could be a component of CAPA (Corrective and Preventive Actions), which aims to address safety concerns.
⚖️ FDA vs. EU MDR Labeling Requirements Comparison Feature: FDA EU MDR UDI Required ✅ Yes ✅ Yes CE Mark ❌ No ✅ Yes IFU ✅ Only if necessary for safe use ✅ Always required Authorized Representative ❌ No ✅ Yes (for non-EU companies)
Language Requirements: Local EU languages ✅ English only
♠️ Labeling Errors Made by Manufacturers
❌ Plagiarism of rivals’ labels without standards verification fulfillment of statements that lack clinical evidence
❌ Not updating labeling in response to design or risk modifications Unable to fulfill EU translation requirements
❌ Misuse of pictograms or omission of necessary symbols
✅ Best Practices for Medical Device Labeling Compliance
✅ Begin with a comprehensive labeling checklist in accordance with FDA and EU MDR regulations.
✅ Regularly review labeling during design modifications or regulatory updates. ✅ Use qualified translators to translate EU IFUs
✅ Standardize symbols to streamline communication.
✅ Conduct cross-functional review (RA/QA, clinical, marketing, and legal) prior to approval. ✅ Maintain labeling records in your technical documentation and design history file.
📚References
- FDA 21 CFR Part 801
- EU MDR 2017/745 Annex I—General Safety and Performance Requirements
- FDA Unique Device Identification (UDI) System
- ISO 15223-1 — Symbols for Medical Device
